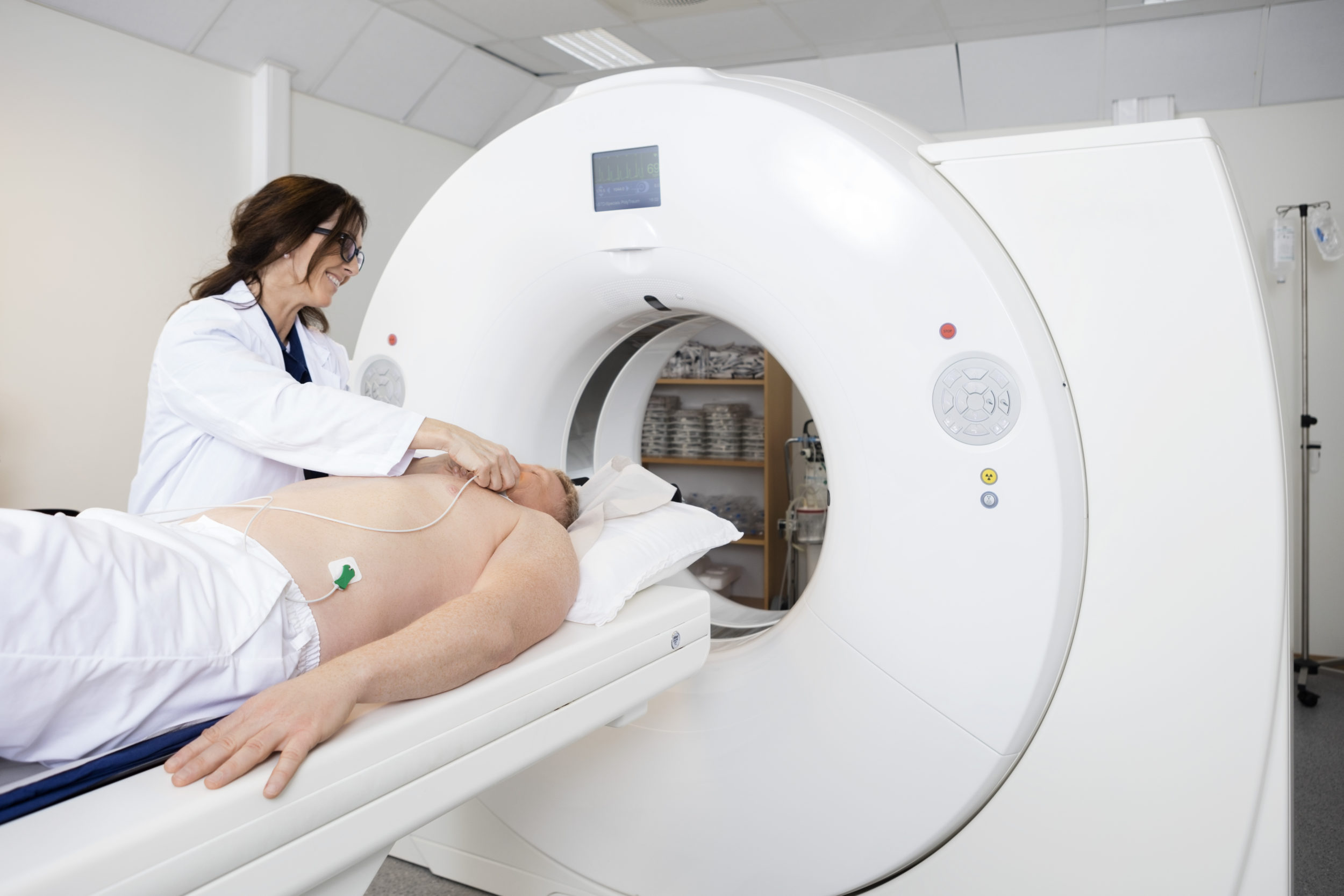
Using computer tomography (CT), a calcium-score screening heart test (also known as a coronary calcium scan) looks for calcium accumulation in the coronary arterial passageway of the heart. A greater coronary calcium score indicates an increased probability of future heart attacks and a higher likelihood of substantial coronary artery constriction. You should know certain things before going for a calcium score screening in Middletown, NJ.
Who has to be screened for calcium scores?
If you are between the ages of 40 and 70 and have an elevated chance of developing heart disease but no symptoms, you might consider getting a calcium scan. Individuals who have the following characteristics are among those who are at higher risk:
- Familial heart disease history
- Smoker, past or present
- High blood cholesterol, hypertension, or high blood pressure in the past
- Overweight
- Inactive way of life
Consider a calcium scan if you are under 40 and have familial hypercholesterolemia, a condition where high cholesterol runs in the family.
Who is not a candidate for a calcium scan?
The arterial calcium test may not be suitable for you if you have been diagnosed with coronary artery disease, have symptoms indicative of coronary heart disease, or have previously had therapy for coronary artery disease. Discuss other methods of testing to identify or track your coronary artery condition with your healthcare practitioner.
What does the calcium score indicate?
The calcium score might be anything between 0 and over 400. It should be taken into account together with other risk factor readings, including blood pressure, cholesterol, obesity, nicotine, family history, and blood sugar levels. If you have any queries concerning the calcium-score monitoring cardiac scan, kindly contact your healthcare practitioner. Your healthcare professional will also discuss the percentile score for your age, gender, and ethnicity.
Discuss calcium screening with your healthcare practitioner if you believe it may be appropriate for you. Your doctor must arrange the calcium monitoring cardiovascular scan to act appropriately depending on the results. Your health care practitioner could suggest a consultation with a cardiologist based on the scan’s findings. If non-cardiac abnormalities are found, proper referrals would be suggested.